Hair Growth Cycle Explained in Simple Words
Hair growth may seem simple on the surface, but it follows a complex biological cycle. Many people panic when they see hair shedding without understanding that some hair fall is normal. Knowing how the hair growth cycle works helps you identify normal shedding, prevent unnecessary worry, and take better care of your hair for long term growth.
Why Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle Matters
Hair does not grow continuously. Each strand follows a fixed cycle of growth, rest, and shedding. When this cycle is disturbed, hair fall increases or growth slows. Understanding the cycle helps you recognize whether hair loss is temporary, lifestyle related, or a sign of a deeper issue.
Overview of the Hair Growth Cycle
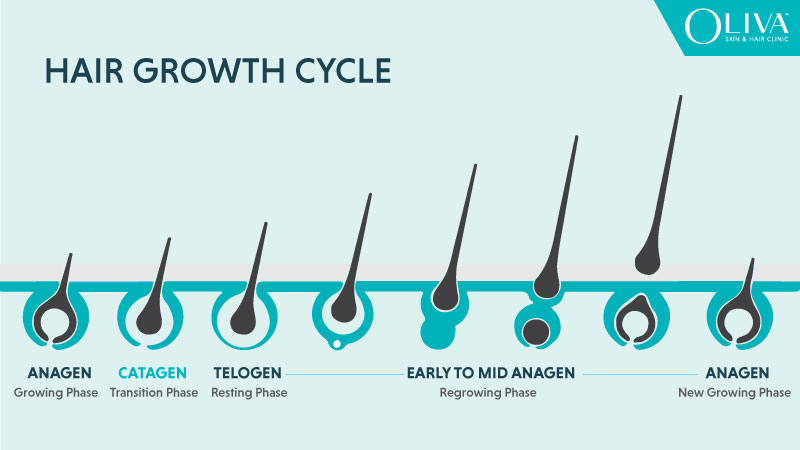
The hair growth cycle has three main stages. These stages are the growth phase, the transition phase, and the resting phase. Every hair strand on your scalp is in a different stage at any given time. This is why you do not lose all your hair at once.
The Anagen Phase: Growth Stage
The anagen phase is the active growth stage of hair. During this phase, hair follicles produce new hair cells rapidly. Hair grows longer and thicker during anagen. This phase can last anywhere from two to seven years depending on genetics, health, and age. The longer the anagen phase, the longer your hair can grow.
Factors Affecting the Anagen Phase
Genetics play the biggest role in determining how long your hair stays in the growth phase. Nutrition, hormones, and scalp health also influence it. Poor diet, stress, illness, and hormonal imbalance can shorten the anagen phase, leading to slower hair growth and increased shedding.
The Catagen Phase: Transition Stage
The catagen phase is a short transition period that lasts about two to three weeks. During this stage, hair growth stops and the follicle begins to shrink. The hair strand detaches from the blood supply but remains in place. This stage prepares the hair for the resting phase.
Why the Catagen Phase Is Important
Although short, the catagen phase is essential for healthy hair cycling. It allows follicles to reset and prepare for new growth. Disruption during this phase can affect the quality of the next hair strand that grows.
The Telogen Phase: Resting Stage
The telogen phase is the resting phase of hair. It lasts around three months. During this time, the hair does not grow but stays attached to the scalp. Around ten to fifteen percent of your hair is usually in the telogen phase at any given time.
Hair Shedding During Telogen Phase
At the end of the telogen phase, hair naturally sheds to make room for new growth. Losing fifty to one hundred hairs per day is considered normal. This shedding does not mean hair loss. It is part of the natural renewal process.
The Exogen Phase: Shedding Process
Some experts also describe a fourth phase called the exogen phase. This is the actual shedding of old hair. New hair begins growing from the follicle as the old hair falls out. Healthy follicles ensure continuous replacement.
What Disrupts the Hair Growth Cycle
Stress, illness, crash dieting, hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, and certain medications can disrupt the hair cycle. These factors can push more hairs into the telogen phase at once. This condition is known as excessive shedding and often occurs a few months after the trigger.
Telogen Effluvium Explained Simply
Telogen effluvium happens when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase together. This leads to sudden hair shedding. It is usually temporary and reversible once the underlying cause is addressed.
How Nutrition Affects the Hair Cycle
Hair follicles need vitamins, minerals, and protein to function properly. Nutrient deficiencies shorten the growth phase and weaken hair strands. Balanced nutrition supports a longer anagen phase and stronger regrowth.
Hormones and the Hair Growth Cycle
Hormones strongly influence hair growth. Thyroid hormones, estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol all affect follicle activity. Hormonal imbalance can shorten the growth phase or delay new growth, leading to thinning and hair fall.
Aging and Hair Growth Changes
As you age, the anagen phase shortens naturally. Hair grows slower and becomes finer. This is a normal process, but good care and nutrition can slow down these changes and maintain hair density longer.
Scalp Health and Hair Cycling
A healthy scalp supports proper blood flow and follicle function. Poor scalp hygiene, infections, or inflammation disrupt the hair cycle. Clean, balanced scalp conditions support continuous growth.
Why Hair Growth Feels Slow
Hair grows about one centimeter per month on average. This slow pace makes changes hard to notice. Hair regrowth requires patience and consistency over several months.
Common Myths About Hair Growth
Cutting hair does not make it grow faster. Washing hair does not increase hair fall beyond normal shedding. Oils and masks support scalp health but cannot change genetics.
How Long It Takes to See Regrowth
After hair shedding, new growth usually starts within three to six months. Visible length and density improvements take longer. Consistency is essential.
Supporting a Healthy Hair Cycle
Eat a balanced diet, manage stress, sleep well, and care for your scalp gently. Avoid harsh treatments and extreme styling. These habits support natural hair cycling.
When Hair Loss Is Not Normal
If hair fall continues for many months, patches appear, or scalp pain occurs, professional evaluation is needed. Not all hair loss is cycle related.
Final Thoughts
The hair growth cycle is a natural and continuous process. Understanding its stages helps you recognize normal shedding and prevent unnecessary worry. Hair health improves when the cycle is supported through nutrition, lifestyle, and gentle care. With patience and consistency, healthy hair growth follows naturally over time.